03. The Role of HRM in Promoting Safety Culture
The safety culture in construction companies is greatly influenced by human resource management. By putting health and safety first, HRM can make sure that safety is ingrained in the culture of the company. This can be accomplished by encouraging employees to raise safety issues, promoting open communication, and rewarding safe conduct.
Implementing Safety-Focused Policies:
- Safety Leadership & HRM
- Safety Training Programs
Regular training sessions should be conducted to educate workers about safety protocols and risk management. HRM practices, particularly training, selection, and employee development, are crucial for occupational health and safety (OHS), according to a large body of research. A recent empirical study in the industrial sector discovered that recruiting and training have a favorable impact on employees' awareness of and involvement in safety initiatives.(Khan et al., 2022)
Implication for HRM: HRM strengthens workers' ability to recognize and respond to safety threats by emphasizing safety in hiring (hiring for safety awareness) and creating role-specific, continuous safety training.
- Defining and Influencing Safety Culture Through HRM
By cultivating leaders who exhibit a clear commitment to safety, encouraging open lines of communication for reporting risks and near misses, and developing performance management systems that reward safe behavior rather than productivity at the expense of safety, HRM also indirectly influences safety culture. HRM makes sure that safety is viewed as a strategic organizational objective rather than as a distinct technical function by including it into HR planning, job design, training frameworks, and leadership development. Over time, these HRM-led interventions assist in changing employee perspectives, enhancing management-employee trust, and fostering a proactive safety culture where workers accept responsibility for safety and continuously give it top priority in their day-to-day work procedures.
- Open Communication Channels
HRM establishes standards for integrity and respect for one another throughout the company by including open communication techniques into grievance procedures, performance management, and safety training initiatives. In the end, when lines of communication are open, workers feel appreciated and empowered to contribute to enhancing workplace safety, which results in more precise reporting of risks, quicker remedial action, and an all-around better, more proactive safety culture.
Kavalela, Ismail, and Rani (2024) found that safety management communications positively influence safety culture through behavioral safety and a perceived working environment.Similarly, a systematic review by Zara and Nordin (2023) identified communication climate and satisfaction as crucial communication dimensions that strengthen safety commitment in high-risk workplaces.
- Recognition and Reward
Acknowledging safe practices can motivate workers to adhere to safety regulations and contribute to an overall safer workplace. By encouraging and maintaining positive safety behaviors, rewards and recognition play a significant motivating role in enhancing organizational safety culture. Employees are more likely to internalize safety as a personal duty rather than just a compliance requirement when they witness that safe actions—such as adhering to protocols, reporting near misses, appropriately utilizing PPE, or proactively detecting hazards—are recognized and praised. This reinforcement system is established by Human Resource Management (HRM) through the design of both formal reward mechanisms, such as safety performance bonuses, certificates, award ceremonies, and recognition programs for "safe worker of the month," and informal practices, such as public recognition during toolbox meetings or verbal praise from supervisors.
In order to prevent underreporting and instead promote honesty and engagement, effective reward systems place equal emphasis on behaviors and participation as well as outcomes (such as zero accidents). In order for employees to view incentives as significant rather than symbolic, HRM also makes sure that recognition is equitable, open, and consistent with company values. Promotional standards that are incorporated into performance evaluation systems
Lee and Kim (2024) found that safety incentives (both rewards and penalties), when paired with behavioral feedback, significantly improve compliance with safety rules. Furthermore, a more psychologically grounded study by Slil, Iyiola, Alzubi & Aljuhmani (2025) shows that employee morale and harmonious safety passion (i.e., internalized commitment to safety) moderate the influence of reward-oriented leadership on safety performance, making recognition more than just transactional.
Reference
Kavalela, A., Ismail, F., & Rani, N. (2024).
Safety management communication and its effect on behavioral safety and perceived working environment. Journal of Safety Communication Studies, 15(1), 55–70.
Khan, M., Ahmed, S., & Ullah, R. (2022).
Impact of recruitment and training on employees’ involvement in safety initiatives in the industrial sector. International Journal of Occupational Health & Training, 9(2), 112–125.
Lee, J., & Kim, S. (2024).
Effects of safety incentives and behavioral feedback on safety compliance. Journal of Applied Safety Psychology, 7(1), 33–49.
Ortega, N., Paes, D., Feng, Z., et al. (2025).
Key determinants of safety culture: A Delphi study of professional safety experts. International Journal of Safety Science & Systems, 18(2), 101–120.
Senthamizh Sankar, S., & Anandh, K. S. (2024).
Safety leadership and safety climate in construction: The mediating role of HRM practices. Journal of Construction Safety Leadership, 12(4), 249–268.
Slil, M., Iyiola, O., Alzubi, K., & Aljuhmani, H. (2025).
Morale, safety passion, and reward-oriented leadership as predictors of safety performance. International Review of Organizational Psychology, 14(1), 77–95.
Zara, S., & Nordin, N. (2023).
Communication climate and satisfaction as predictors of safety commitment in high-risk workplaces: A systematic review. Safety & Communication Review, 11(3), 200–218.

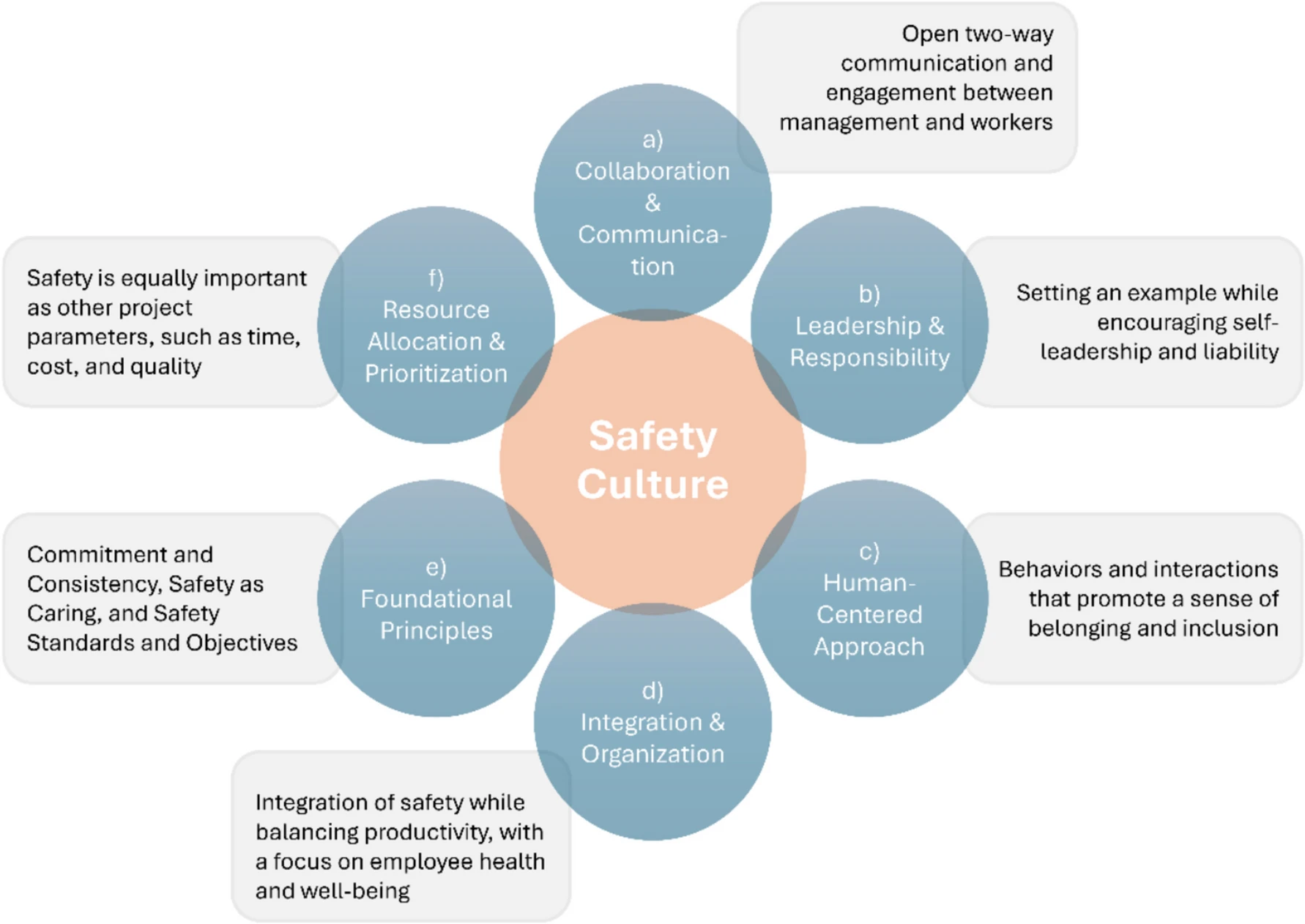
This highlights the pivotal role of HRM in embedding a proactive safety culture within construction companies. By aligning HR practices with safety objectives, organizations can move beyond mere compliance and create a work environment where safety becomes a shared responsibility. The research by Senthamizh Sankar and Anandh (2024) underscores that transformational safety leadership is a critical driver: when supervisors demonstrate commitment, communicate openly, and actively support safety training, it strengthens employees’ perception of the safety climate. HRM can reinforce this by integrating safety-focused leadership development, recognition programs for safe behaviors, and structured channels for reporting hazards. Ultimately, a combination of HR-driven policies and effective safety leadership cultivates a culture where safety is internalized as a core organizational value rather than a checklist obligation.
ReplyDeleteIt successfully demonstrates how HRM and excellent safety leadership collaborate to create a proactive safety culture—one in which everyone embraces safety, it is actually valued, and it is reinforced through training and recognition rather than being viewed as merely compliance. Thank you Apeksha
DeleteA thorough and practical guide to how HRM shapes safety culture in construction. You clearly show that safety-focused policies, transformational leadership, ongoing training, open communication, and thoughtful recognition are all essential to building a proactive and engaged safety environment. The empirical evidence and recommendations reinforce the idea that HR’s strategic alignment with safety empowers employees, strengthens trust, and makes safety an integrated part of daily work. Excellent insights for leaders and HR professionals aiming for lasting impact!
ReplyDeleteThank you Sachithra
DeleteYour article provides a comprehensive explanation of how HRM strengthens safety culture through leadership, training, communication, and recognition systems.
ReplyDeleteIt effectively connects research evidence with practice, showing how HR-led policies shape employee behaviour, safety awareness, and organisational commitment.
The discussion highlights HRM’s strategic role in embedding safety into recruitment, development, performance management, and daily operations.
Overall, it reinforces that a strong safety culture depends on HRM’s ability to integrate safety values across systems, leadership practices, and workforce engagement.
Thank you for your encouragement Rahal
ReplyDeleteThis section shows clearly the central role played by HRM in fostering a proactive safety culture within Sri Lanka's construction sector. HRM influences safety culture through safety-focused policies, leadership development, continuous training, open channels of communication, and recognition and reward systems. Embedding safety into recruitment, training, leadership, performance management, and feedback, HRM ensures safety becomes an active organizational value rather than a compliance obligation. Effective practices of HRM instill accountability, trust, and engagement among workers, leading to a more vigilant and safety-conscious workforce with fewer workplace accidents.
ReplyDelete